大文件上传
文件上传基础
首先,我们需要熟悉一下基本的文件上传流程:
html
<!doctype html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8" />
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0" />
<title>Document</title>
</head>
<body>
<input
type="file"
id="file"
label="选择文件"
title="Choose a file"
placeholder="No file chosen"
/>
<script>
const file = document.getElementById('file');
file.onchange = (e) => {
const file = e.target.files[0];
const piece = file.slice(0, 45);
if (!file) return;
console.log('🚀 ~ file.html:20 ~ file:', file);
console.log('🚀 ~ file.html:22 ~ piece:', piece);
};
</script>
</body>
</html>我们可以通过 slice 方法将文件按字节分割,得到 Blob 对象,并将其输出观察:
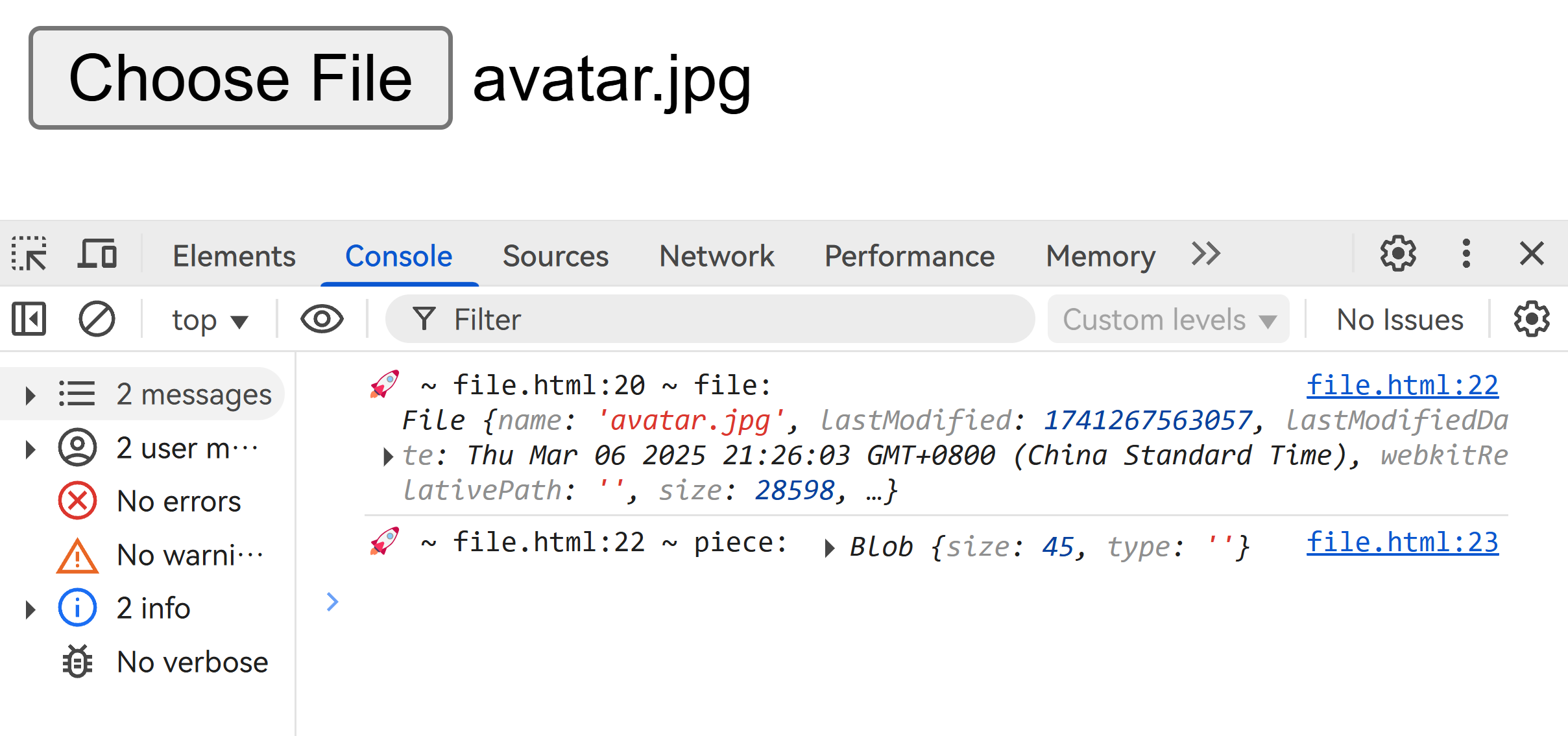
分片上传
既然如此,我们就可以封装切片函数来达到分片上传的目的:
js
function createChunks(file, chunkSize) {
const chunks = [];
let offset = 0;
while (offset < file.size) {
chunks.push(file.slice(offset, offset + chunkSize));
offset += chunkSize;
}
return chunks;
}效果如下:
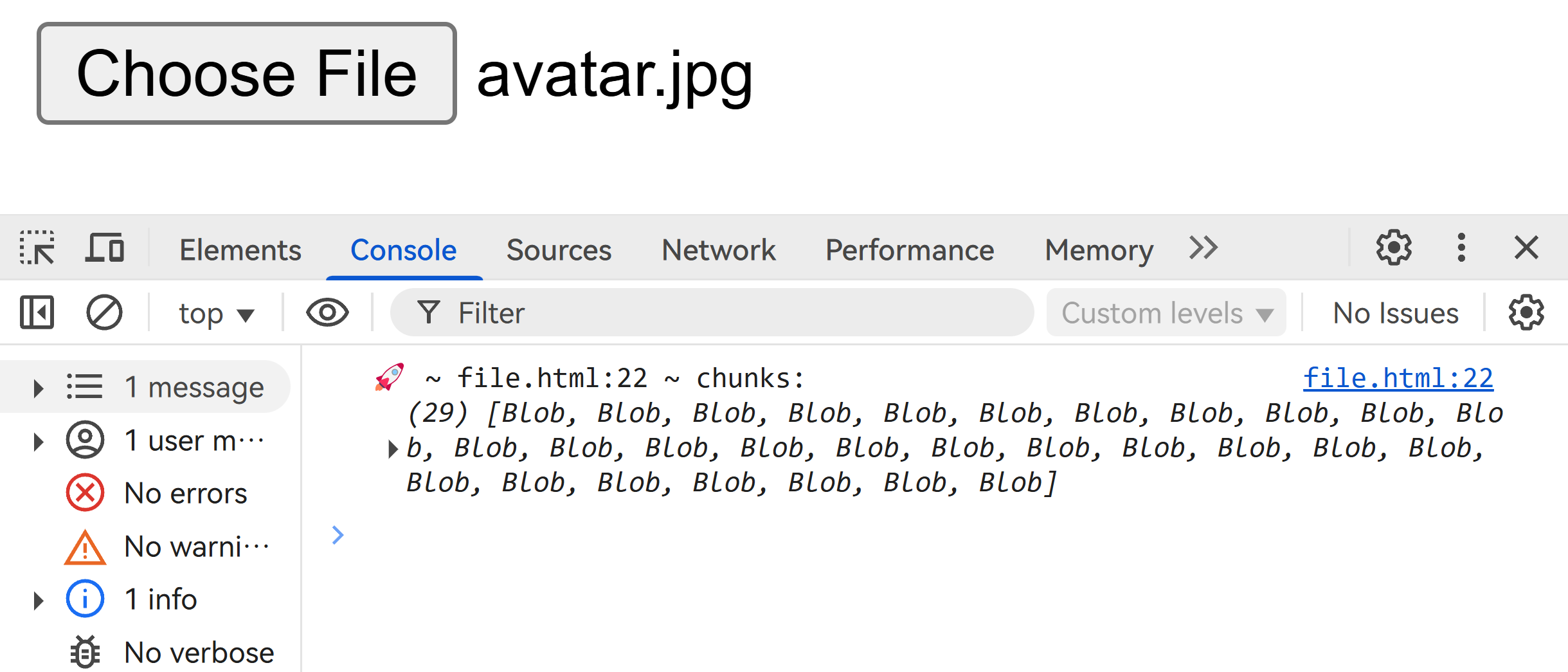
信息
文件分片很快,无论你文件多大都会瞬间成功。这是因为,分片仅仅只是一次数学运算,File 和 Blob 都不涉及文件数据。
断点续传
断点续传,顾名思义,就是上传过程中断开,下次再传的时候,从上次中断的地方继续上传。
这一步的实现需要发起请求,客户端告诉服务器“这个文件上传到哪里了”,服务器返回“我还需要 a 到 b 范围内字节的数据”。
这就出现问题了——怎么表示“这个文件”?文件名是可能重复的啊!发绝对路径给服务器吗?那如果路径变化了呢?我的文件发生过移动呢?
解决方案就是,你要找到每个文件的唯一标识,所以我们可以采用 md5 来生成文件唯一标识。
接下来的任务就是编写文件标识函数,当然,我们需要采用增量算法,不要忘记正在处理大文件上传的背景:
html
<!doctype html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8" />
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0" />
<title>Document</title>
<script src="https://cdnjs.cloudflare.com/ajax/libs/spark-md5/3.0.2/spark-md5.min.js"></script>
</head>
<body>
<input
type="file"
id="file"
label="选择文件"
title="Choose a file"
placeholder="No file chosen"
/>
<script>
const file = document.getElementById('file');
file.onchange = (e) => {
const file = e.target.files[0];
if (!file) return;
const chunks = createChunks(file, 1024);
hash(chunks);
};
function createChunks(file, chunkSize) {
const chunks = [];
let offset = 0;
while (offset < file.size) {
chunks.push(file.slice(offset, offset + chunkSize));
offset += chunkSize;
}
return chunks;
}
function hash(chunks) {
const spark = new SparkMD5();
function _read(i) {
if (i >= chunks.length) {
console.log('🚀 ~ file.html:41 ~ spark.end():', spark.end());
return;
}
const reader = new FileReader();
const blob = chunks[i];
reader.onload = (e) => {
const bytes = e.target.result;
spark.append(bytes);
_read(i + 1);
};
reader.readAsArrayBuffer(blob);
}
_read(0);
}
</script>
</body>
</html>效果如下:
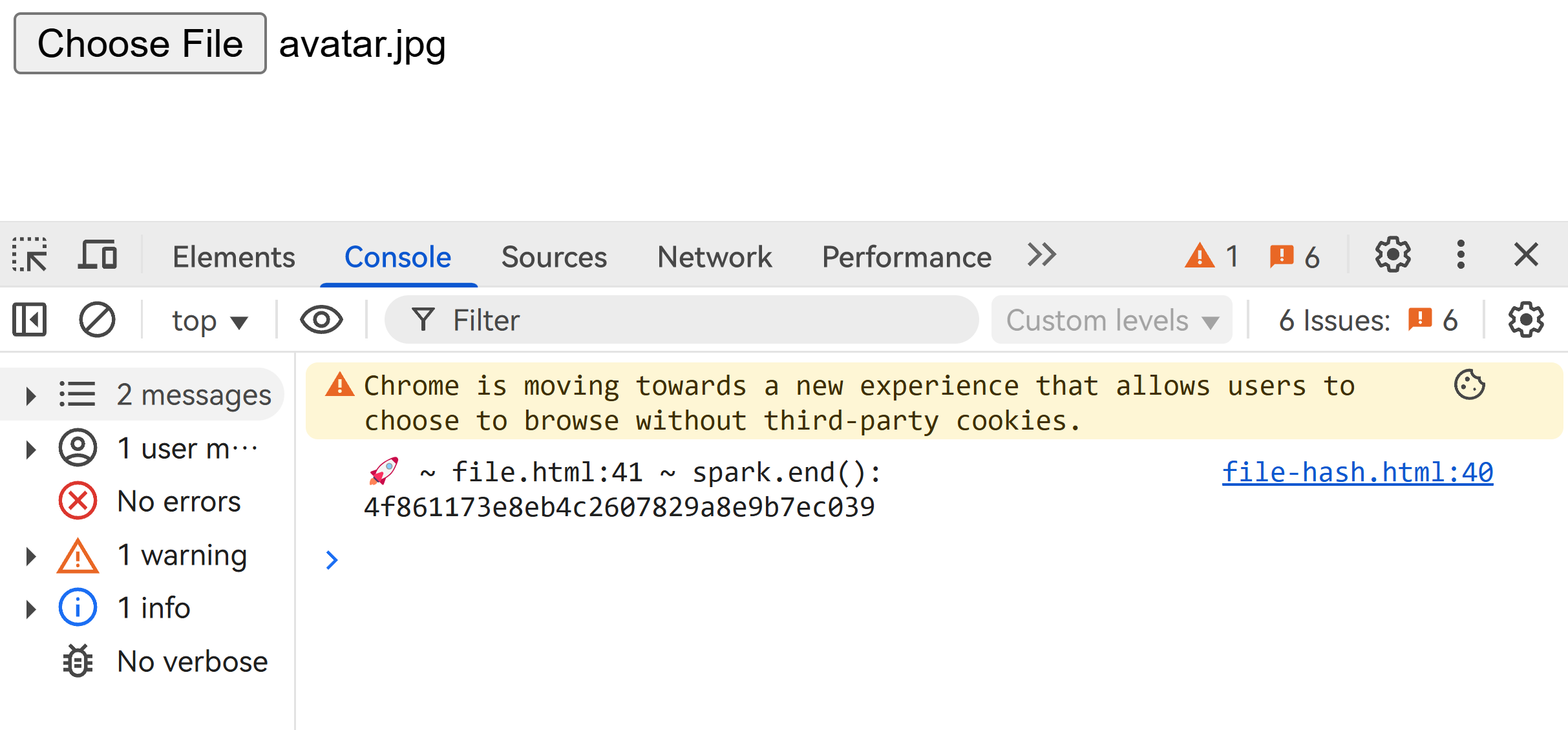
我们接下来把它封装成异步函数,因为这样的操作是消耗时间的:
js
async function hash(chunks) {
return new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
const spark = new SparkMD5();
function _read(i) {
if (i >= chunks.length) {
resolve(spark.end());
return;
}
const reader = new FileReader();
const blob = chunks[i];
reader.onload = (e) => {
const bytes = e.target.result;
spark.append(bytes);
_read(i + 1);
};
reader.readAsArrayBuffer(blob);
}
_read(0);
});
}写到这一步,附上一版临时代码以供参考:
html
<!doctype html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8" />
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0" />
<title>Document</title>
<script src="https://cdnjs.cloudflare.com/ajax/libs/spark-md5/3.0.2/spark-md5.min.js"></script>
</head>
<body>
<input
type="file"
id="file"
label="选择文件"
title="Choose a file"
placeholder="No file chosen"
/>
<script>
const file = document.getElementById('file');
file.onchange = async (e) => {
const file = e.target.files[0];
if (!file) return;
const chunks = createChunks(file, 1024);
const spark = await hash(chunks);
console.log('🚀 ~ file.html:41 ~ spark.end():', spark);
};
function createChunks(file, chunkSize) {
const chunks = [];
let offset = 0;
while (offset < file.size) {
chunks.push(file.slice(offset, offset + chunkSize));
offset += chunkSize;
}
return chunks;
}
async function hash(chunks) {
return new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
const spark = new SparkMD5();
function _read(i) {
if (i >= chunks.length) {
resolve(spark.end());
return;
}
const reader = new FileReader();
const blob = chunks[i];
reader.onload = (e) => {
const bytes = e.target.result;
spark.append(bytes);
_read(i + 1);
};
reader.readAsArrayBuffer(blob);
}
_read(0);
});
}
</script>
</body>
</html>